




|
Franchises available nationally click here » |


![Text Box: [ Brain Health & Counselling ] [ Stress Release Acupuncture ] [ Auricular Detoxification ]
[ Acupuncture for ADD & ADHD ] [ Acupuncture for Smoking Cessation ] [ Magnotherapy ] [ Electro Stimulation ]
[ N.A.D.A. ] [ HOME ]](image664.gif)
|
Introduction Yin and Yang is one of the most fundamental concepts in Traditional Chinese Medicine, as it is the foundation of diagnosis and treatment. The earliest reference to Yin and Yang is in the I Ching (Book of Changes) in approximately in 700 BC. In this work, all phenomena are said to be reduced to Yin-Yang.
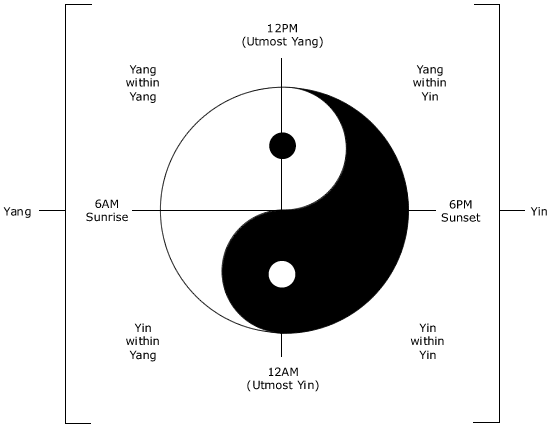
1. Yin-Yang are opposites They are either on the opposite ends of a cycle, like the seasons of the year, or, opposites on a continuum of energy or matter. This opposition is relative, and can only be spoken of in relationships. For example: Water is Yin relative to steam but Yang relative to ice. Yin and Yang are never static but in a constantly changing balance. 2. Interdependent: Can not exist without each other The Tai Ji (Supreme Ultimate) diagram shows the relationship of Yin & Yang and illustrates interdependence on Yin & Yang. Nothing is totally Yin or totally Yang. Just as a state of total Yin is reached, Yang begins to grow. Yin contains seed of Yang and vise versa. They constantly transform into each other. For Example: no energy without matter, no day without night. The classics state: "Yin creates Yang and Yang activates Yin". 3. Mutual consumption of Yin and Yang Relative levels of Yin Yang are continuously changing. Normally this is a harmonious change, but when Yin or Yang are out of balance they affect each other, and too much of one can eventually weaken (consume) the other.
Four (4) possible states of imbalance: 1. Preponderance (Excess) of Yin 2. Preponderance (Excess) of Yang 3. Weakness (Deficiency) of Yin 4. Weakness (Deficiency) of Yang
4. Inter-transformation of Yin and Yang. One can change into the other, but it is not a random event, happening only when the time is right. For example: Spring only comes when winter is finished.
Yin and Yang Theory and History Yin Yang is the fundamental principle, and the most important theory in TCM, underlying all physiology, pathology & treatment.
Combining the two, we have the four stages of Yin and Yang
With addition of an extra line, the Eight Trigrams (Ba Gua) were formed, illustrating all the directions .
The Eight Trigrams were combined to form 64 hexagrams, symbolizing all possible phenomena of the Universe.
Yin Yang had been understood for many centuries, but was systematically elaborated and written down by Tsou Yen of the Yin Yang (Naturalist) School in the Warring States Period (476-221 BC). 5 Element Theory was developed at same time.
The Naturalist school promoted idea of living in harmony with natural laws. Scholars of this school interpreted natural phenomena and observed how these are reflected in the human body in health and disease. Yin and Yang and the Five Elements became an integral part of Chinese philosophy.
24 Hour Yin Yang Cycle
General Qualities of Yin and Yang
These transform into one another. They are 2 states of a continuum. For Example: Liquid water (Yin) heat - vapor (Yang) - cools - liquid (Yin).
All physiological processes, signs and symptoms can be reduced to Yin-Yang. In general, every treatment modality aims to:
Tonify Yang Tonify Yin Disperse excess Yang Disperse excess Yin
(In practice, depending on the condition, strategies may be combined, for example: disperse excess Yin & tonify Yang)
Yin and Yang and the Six Pathogenic Factors
Yin and Yang and the Human Body
Front and Back
Front is more soft and vulnerable (Yin). Back contains spine that holds ribs: protection. When human depicted as crouching, back receives sun (Yang) and front faces the earth (Yin), is in shade and is protected.
All Yang channels (except the Stomach channel) flow on the dorsal or dorsolateral surface of the trunk and limbs. They carry Yang energy and protect the body from pathogenic factors. Yin channels flow on the anterior or anteromedial surface of the trunk and limbs.
Body and Head
Interior and Exterior
Below the waist and Above the Waist
Anterior/Medial and Posterior/Lateral Surface of the Limbs
Structure and Function
Blood, Body Fluids, and Qi
Note: there are several types of Qi. Each is relatively more Yin or Yang.
Conservation/Store (Yin) and Transformation/Change (Yang)
Solid and Hollow Organs (Zang Fu)
Yang Organs are "Hollow": receive and circulate but do not store, involved in digestion, transformation, excretion. sore throats, nosebleeds, irritability, manic behavior. b.) Yang does not warm and activate Yin (cold limbs, hypo-activity, poor circulation of blood, pale face, low energy. Actual symptoms depend on specific pathologies, which Organ involved, etc.
Yin and Yang in Pathology
Clinical signs and symptoms can be interpreted via Yin-Yang theory. When Yin Yang are in dynamic balance and relating harmoniously, there are no symptoms to observe. When Yin and Yang are out of balance, they become separated.
|
|
TCM pg.1 |
|
Yin
|
Yang
|
|
|
Wind |
|
Cold |
Heat |
|
Dampness |
Dryness |
|
|
Summer heat |
|
Yin
Translations:
1. female, passive, negative principle in nature 2. the moon 3. shaded orientation 4. north or shady side of a hill 5. south of a river. |
Yang
Translations:
1. positive, active, male principle in nature 2. south or sunny side of a hill 3. north of a river. |
|
Yin
|
Yang
|
|
Darkness |
Light |
|
Moon |
Sun |
|
Feminine |
Masculine |
|
Shade |
Brightness |
|
Rest |
Activity |
|
West (Sunset = Yin) |
East (Sunrise = beginning of Yang) |
|
North |
South |
|
Earth |
Heaven |
|
Right |
Left |
|
Flat (like Earth) |
Round (like Heaven) |
|
Matter |
Energy |
|
More material/dense |
Non-material, rarefied |
|
Yin
|
Yang
|
|
Produces form |
Produces energy |
|
Grows |
Generates |
|
Substantial |
Non-substantial |
|
Matter |
Energy |
|
Contraction |
Expansion |
|
Descending |
Rising |
|
Below |
Above |
|
Water |
Fire |

